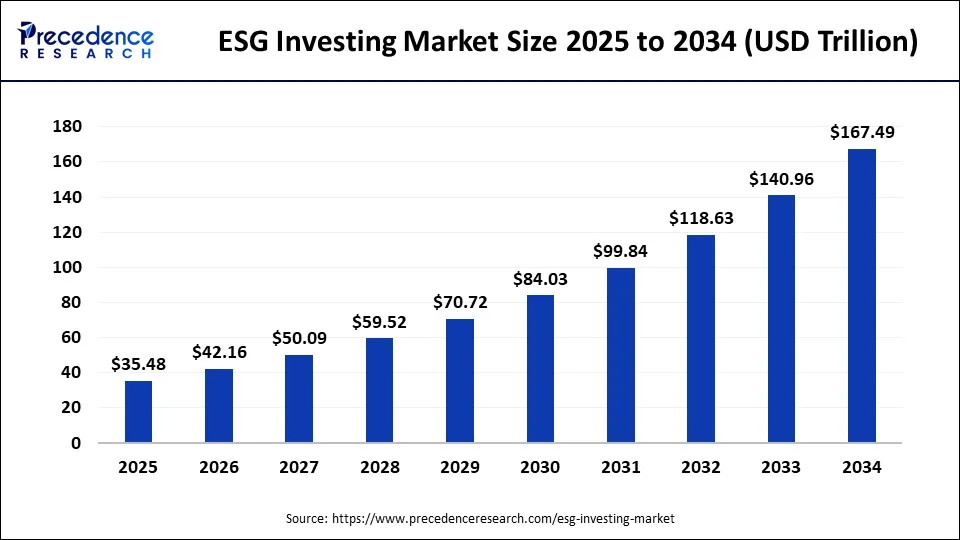
As the financial landscape evolves, more investors are recognizing the significance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria in shaping investment decisions. In the United States, where a growing awareness of corporate responsibility is taking root, mid-career professionals aged 35-45 find themselves at a pivotal point in their investment strategies. ESG investing emphasizes not just financial returns but also the broader societal impact of investments, which resonates deeply with a generation increasingly concerned about sustainability.
In the current economic environment, ESG investing is becoming a crucial element in portfolio management. Investors are focusing on companies that prioritize sustainability practices—like reducing carbon footprints and promoting diversity—while still delivering competitive returns. The appeal lies in the dual benefit: achieving financial growth while contributing positively to society and the environment.
The Evolution of ESG Investing
Historically, socially responsible investing (SRI) emerged in the 1960s when investors began avoiding companies linked to tobacco or arms production. The concept has since transformed into ESG investing, supported by frameworks like the UN Principles for Responsible Investment established in 2006. These principles encourage institutional investors to integrate ESG factors into their strategies.
With trillions of dollars now managed under ESG principles, this investment approach has transitioned from niche to mainstream. Major asset managers recognize that integrating ESG factors can mitigate long-term risks and enhance brand reputation. For instance, companies dedicated to renewable energy are viewed as more resilient investments compared to those reliant on fossil fuels.
The Rise of Green Finance
Green finance has gained traction alongside ESG investing, providing targeted funding for environmentally beneficial projects. This includes green bonds and climate funds focused on renewable energy, energy efficiency technologies, and sustainable agriculture. The introduction of standards like the Green Bond Principles has fostered greater transparency and accountability in green financing.
American institutions are increasingly adopting these frameworks, aligning their investment strategies with global sustainability goals such as those outlined in the Paris Climate Agreement. For mid-career investors, this creates an opportunity to participate in the burgeoning green economy while supporting initiatives that resonate with their personal values.
Interconnection Between ESG and Green Finance
ESG investing and green finance are intrinsically linked, both striving towards similar goals of fostering sustainability and ethical governance. Investors who prioritize ESG criteria often gravitate towards green financial instruments. For example, purchasing green bonds issued by companies demonstrating strong governance can be both a sound financial decision and an ethical one.
This integration underscores a shift from short-term profit maximization towards long-term value creation. It encourages resilience against climate change and other systemic risks while promoting sustainable economic growth—a narrative that aligns perfectly with the aspirations of mid-career professionals seeking meaningful investments.
Benefits and Challenges
While the growth of ESG investing is promising, challenges remain. Issues like lack of standardization in ESG ratings and the risk of greenwashing—where companies exaggerate their sustainability claims—pose potential pitfalls for investors. Nonetheless, research indicates that companies adhering to ESG standards tend to outperform their peers over time due to improved operational efficiencies and stakeholder trust.
Mid-career investors should navigate these challenges by seeking transparency and ensuring their investments align with genuine sustainability practices. Tools such as ESG ratings from reputable sources can help demystify these complexities.
The Future of ESG Investing
The future of investing is undoubtedly leaning towards sustainability. As artificial intelligence enhances data accuracy and blockchain ensures transaction transparency, ESG integration will likely become a standard practice rather than an option. Governments are expected to incentivize sustainable lending practices further, thereby fostering an investment environment that prioritizes long-term wellbeing over short-term gains.
Investors will increasingly be evaluated not only by their financial success but also by their contributions to societal welfare. This represents a significant paradigm shift in how capital markets function—making it essential for mid-career professionals to adapt their investment strategies accordingly.
In conclusion, embracing ESG investing is not just about following a trend; it is about aligning one’s financial decisions with a broader vision for sustainability and corporate responsibility. As more organizations adopt these principles, mid-career investors stand to benefit from both financial returns and the satisfaction of contributing to a more sustainable future.
