As we approach 2025, the U.S. stock market is witnessing a significant sector rotation that could redefine investment strategies for many investors. This shift is not merely a reflection of changing consumer preferences but is deeply intertwined with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors that are reshaping capital flows and asset valuations across industries. The transition from high-carbon to low-carbon assets is accelerating, driven by regulatory pressures and evolving investor expectations regarding sustainability.
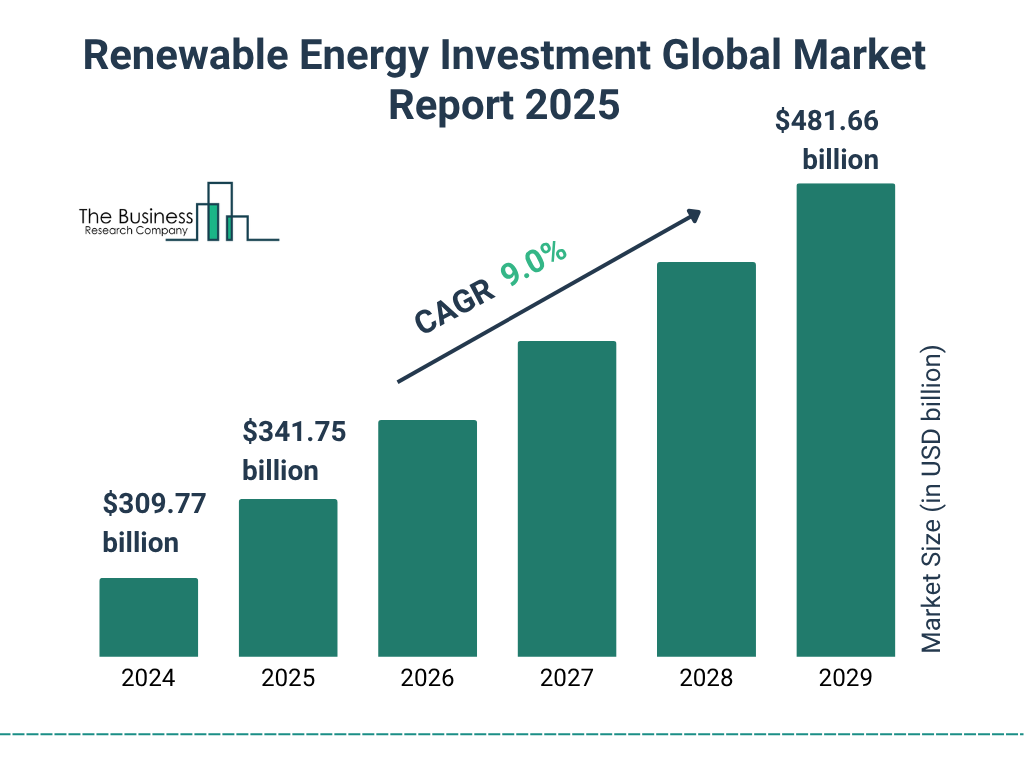
The recent surge in clean energy investments underscores this trend. According to Bloomberg, global spending on renewable energy technologies reached record levels in 2023, highlighting a robust commitment to decarbonization amid rising climate concerns. This influx of capital into renewables has led to a revaluation of traditional energy companies, particularly those heavily reliant on fossil fuels. As institutional investors increasingly prioritize ESG criteria in their portfolios, the valuation gap between high-emission sectors and their cleaner counterparts continues to widen.
In this context, understanding the implications of ESG ratings becomes crucial for investors navigating these turbulent waters. Companies with strong governance structures and transparent reporting practices are likely to attract more capital as they mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance and reputational damage. A recent analysis from Reuters indicates that firms demonstrating superior ESG performance often enjoy lower cost of capital and higher valuation multiples compared to their peers with weaker governance frameworks.
The societal dimension of ESG also plays a pivotal role in shaping investment decisions. Investors are becoming more aware of labor practices within supply chains and the broader social impact of corporate activities. Companies that fail to address these issues may face backlash from consumers and investors alike, leading to potential declines in market value. As highlighted by CNBC, firms that proactively engage with stakeholders on social issues tend to foster greater loyalty among customers and employees, ultimately translating into better financial performance.
Moreover, the rise of green bonds and sustainable-linked debt instruments reflects an evolving landscape where financing mechanisms align with environmental objectives. Institutional demand for green bonds has surged as investors seek opportunities that not only provide returns but also contribute positively to environmental outcomes. MarketWatch recently reported that green bond issuance reached unprecedented levels in 2023, indicating a growing appetite among fixed-income investors for sustainable investment options.
Institutional investor behavior is also shifting under the weight of regulatory scrutiny surrounding ESG disclosures and fiduciary responsibilities. Major asset managers like BlackRock have emphasized integrating sustainability into their investment processes as part of their long-term strategy. This shift towards responsible investing is further reinforced by policy developments such as the Inflation Reduction Act which incentivizes clean technology adoption through tax credits and subsidies aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
The interplay between macroeconomic factors—such as inflation rates, interest rates, employment figures—and sector performance cannot be overlooked either. Rising interest rates can dampen growth prospects for highly leveraged companies while simultaneously making fixed-income securities more attractive relative to equities. In this environment, sectors poised for growth due to structural changes—like technology firms focused on low-carbon innovations—may outperform traditional industries burdened by legacy costs associated with high emissions.
As we look ahead towards 2025, it becomes evident that sector rotation will not only redefine individual company valuations but also reshape entire industry landscapes based on their alignment with sustainable practices. Investors must remain vigilant about how these dynamics play out across various sectors—from clean energy initiatives gaining traction against traditional oil giants—to tech companies innovating around sustainability metrics.
This evolving narrative presents both challenges and opportunities for middle-class investors seeking stable returns amidst volatility while balancing time management constraints inherent in full-time careers. By adopting a long-term perspective centered around sustainable capital allocation principles informed by deep insights into ESG trends—investors can position themselves advantageously within this transformative market landscape.
For those looking to deepen their understanding of how sector rotations influenced by ESG considerations will shape future investment strategies over time, I invite you to explore our comprehensive insights at this link. Embracing a long-term view coupled with sustainable capital allocation can yield significant benefits.
